Give Examples Of Animals That Excrete Ammonia As Such,, Or As Urea Or Uric Acid?
Osmotic Regulation and Excretion
218 Nitrogenous Wastes
Learning Objectives
Past the end of this section, yous volition be able to exercise the following:
- Compare and dissimilarity the way in which aquatic animals and terrestrial animals can eliminate toxic ammonia from their systems
- Compare the major byproduct of ammonia metabolism in vertebrate animals to that of birds, insects, and reptiles
Of the 4 major macromolecules in biological systems, both proteins and nucleic acids contain nitrogen. During the catabolism, or breakdown, of nitrogen-containing macromolecules, carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are extracted and stored in the class of carbohydrates and fats. Excess nitrogen is excreted from the body. Nitrogenous wastes tend to course toxic ammonia, which raises the pH of trunk fluids. The formation of ammonia itself requires free energy in the form of ATP and large quantities of water to dilute it out of a biological arrangement. Animals that live in aquatic environments tend to release ammonia into the water. Animals that excrete ammonia are said to be ammonotelic. Terrestrial organisms have evolved other mechanisms to excrete nitrogenous wastes. The animals must detoxify ammonia by converting it into a relatively nontoxic form such every bit urea or uric acrid. Mammals, including humans, produce urea, whereas reptiles and many terrestrial invertebrates produce uric acid. Animals that secrete urea as the main nitrogenous waste textile are called ureotelic animals.
Nitrogenous Waste matter in Terrestrial Animals: The Urea Cycle
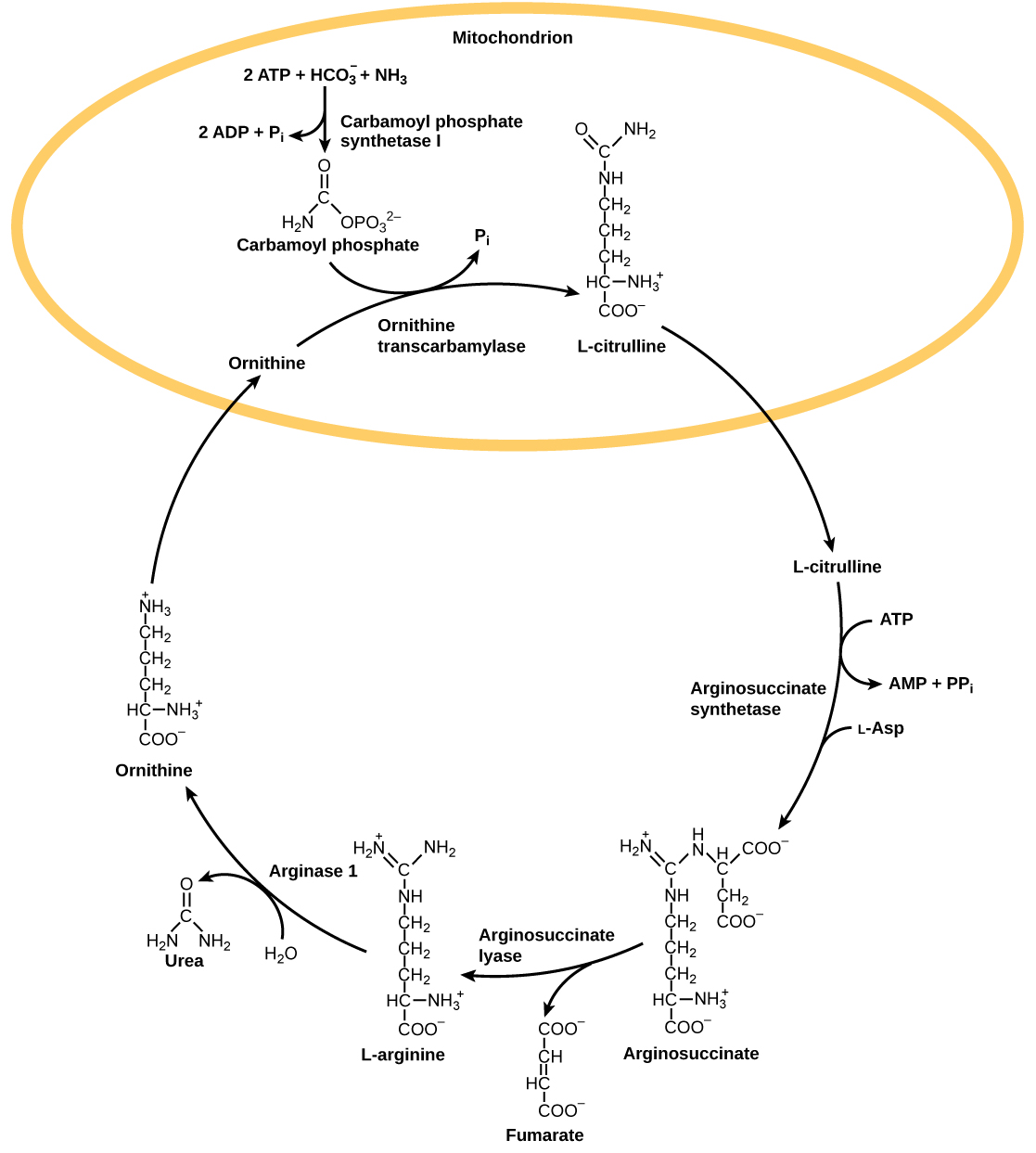
The urea bicycle is the chief mechanism by which mammals convert ammonia to urea. Urea is made in the liver and excreted in urine. The overall chemical reaction by which ammonia is converted to urea is ii NHthree (ammonia) + COii + 3 ATP + H2O → H2Northward-CO-NHii (urea) + 2 ADP + 4 Pi + AMP.
The urea cycle utilizes v intermediate steps, catalyzed past five different enzymes, to convert ammonia to urea, as shown in (Effigy). The amino acid 50-ornithine gets converted into different intermediates earlier being regenerated at the end of the urea cycle. Hence, the urea cycle is also referred to as the ornithine bike. The enzyme ornithine transcarbamylase catalyzes a key pace in the urea wheel and its deficiency tin can lead to accumulation of toxic levels of ammonia in the trunk. The first two reactions occur in the mitochondria and the last iii reactions occur in the cytosol. Urea concentration in the blood, called claret urea nitrogen or BUN, is used as an indicator of kidney function.
The urea cycle converts ammonia to urea.
Evolution Connection
Excretion of Nitrogenous WasteThe theory of evolution proposes that life started in an aquatic environment. It is not surprising to run across that biochemical pathways like the urea cycle evolved to suit to a changing environment when terrestrial life forms evolved. Arid conditions probably led to the development of the uric acrid pathway as a means of conserving water.
Nitrogenous Waste material in Birds and Reptiles: Uric Acid
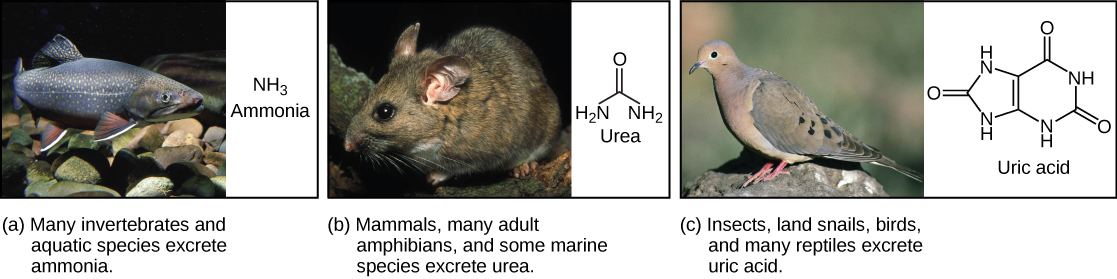
Birds, reptiles, and most terrestrial arthropods catechumen toxic ammonia to uric acid or the closely related chemical compound guanine (guano) instead of urea. Mammals also form some uric acid during breakdown of nucleic acids. Uric acid is a compound like to purines found in nucleic acids. It is h2o insoluble and tends to grade a white paste or powder; it is excreted by birds, insects, and reptiles. Conversion of ammonia to uric acrid requires more free energy and is much more than complex than conversion of ammonia to urea (Figure).
Nitrogenous waste matter is excreted in different forms by dissimilar species. These include (a) ammonia, (b) urea, and (c) uric acid. (credit a: modification of piece of work by Eric Engbretson, USFWS; credit b: modification of piece of work by B. "Moose" Peterson, USFWS; credit c: modification of work past Dave Menke, USFWS)
Everyday Connection
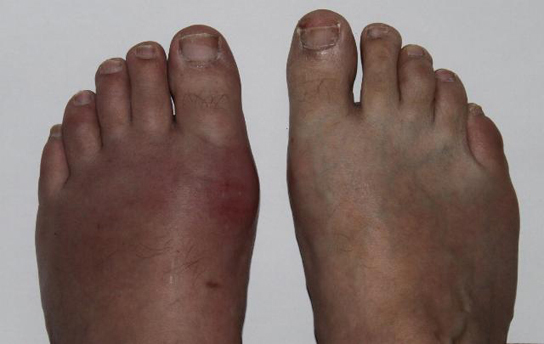
GoutMammals use uric acrid crystals as an antioxidant in their cells. Nonetheless, too much uric acid tends to form kidney stones and may also cause a painful condition called gout, where uric acid crystals accumulate in the joints, as illustrated in (Figure). Food choices that reduce the amount of nitrogenous bases in the nutrition assist reduce the take a chance of gout. For example, tea, coffee, and chocolate have purine-similar compounds, called xanthines, and should be avoided by people with gout and kidney stones.
Gout causes the inflammation visible in this person'southward left big toe articulation. (credit: "Gonzosft"/Wikimedia Commons)
Section Summary
Ammonia is the waste material produced by metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds like proteins and nucleic acids. While aquatic animals tin can easily excrete ammonia into their watery surroundings, terrestrial animals have evolved special mechanisms to eliminate the toxic ammonia from their systems. Urea is the major byproduct of ammonia metabolism in vertebrate animals. Uric acrid is the major byproduct of ammonia metabolism in birds, terrestrial arthropods, and reptiles.
Review Questions
BUN is ________.
- blood urea nitrogen
- blood uric acid nitrogen
- an indicator of blood volume
- an indicator of blood pressure
A
Human being beings accumulate ________ before excreting nitrogenous waste matter.
- nitrogen
- ammonia
- urea
- uric acid
C
Disquisitional Thinking Questions
In terms of evolution, why might the urea wheel have evolved in organisms?
It is believed that the urea cycle evolved to conform to a changing surround when terrestrial life forms evolved. Arid conditions probably led to the development of the uric acid pathway as a means of conserving water.
Compare and contrast the germination of urea and uric acid.
The urea wheel is the primary machinery by which mammals convert ammonia to urea. Urea is made in the liver and excreted in urine. The urea bicycle utilizes five intermediate steps, catalyzed by five different enzymes, to convert ammonia to urea. Birds, reptiles, and insects, on the other manus, catechumen toxic ammonia to uric acrid instead of urea. Conversion of ammonia to uric acrid requires more energy and is much more circuitous than conversion of ammonia to urea.
Glossary
- ammonia
- compound made of i nitrogen atom and three hydrogen atoms
- ammonotelic
- describes an animal that excretes ammonia as the primary waste matter material
- antioxidant
- agent that prevents cell destruction past reactive oxygen species
- blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
- estimate of urea in the blood and an indicator of kidney function
- urea cycle
- pathway by which ammonia is converted to urea
- ureotelic
- describes animals that secrete urea every bit the principal nitrogenous waste material fabric
- uric acid
- byproduct of ammonia metabolism in birds, insects, and reptiles
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/biology2eopenstax/chapter/nitrogenous-wastes/
Posted by: montanoyousticheare.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Give Examples Of Animals That Excrete Ammonia As Such,, Or As Urea Or Uric Acid?"
Post a Comment