What Is A Filter In Electrical Engineering
Different Types of Filters & Their Applications
Introduction to Filters
A frequency filter or also known as a frequency selective circuit is a special type of a circuit, which is used for filtering out some of the input signals on the basis of their frequencies.
A filter circuit passes some frequency signal's without any attenuation (Reduction in amplitude) or with some amplification, & attenuate other frequency depending on the types of the filter.
Terms Used in Filters
To empathize the frequency response of a filter, you need to have an idea well-nigh the terms used in information technology. Some of the terms used in describing the characteristics of a filter are given beneath;
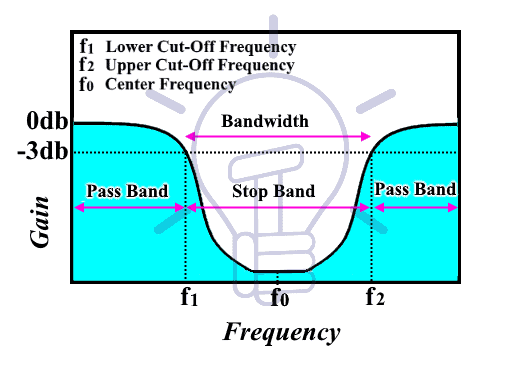
Passband
The band of frequencies of the input signal that pass through the filter without whatsoever attenuation is chosen Passband. Usually, the Passband has no gain considering the filter is a passive filter. In active-filters, the passband may have some proceeds depending on the configuration of the circuit.
Passband lies earlier the cutoff frequency (mentioned below).
- Related Post: Types of Passive High Pass Filters
Stopband
The band of frequencies of the input signal that are blocked or attenuated in the filter is called Stopband.the gain at the stop is commonly taken to be less than -3db of the input.
-3db proceeds is considered for the 1st order filter. second order filter has -6db gain, which decreases with the order of the filter.
- Related Post: Types of Active Low Pass Filters
Cutoff Frequency
The passband & stopband are distinguished from each other by the cutoff frequency or corner frequency. The output indicate's voltage at the cutoff frequency is 70.7% of the input signal'southward voltage. Information technology is also known as "-3db frequency" because -3db represents half power. And it is the frequency where the ability of the output signal becomes half the power of the input signal.
In a ring pass or band turn down filter, at that place are two cutoff frequencies.
-
Lower Cutoff Frequency:
The lower frequency at which the proceeds of the filter is half or -3db. It is denoted by f1. Bandpass filter allows frequency later on this betoken, whereas the band stop filter blocks information technology.
-
Upper Cutoff Frequency
The upper frequency at which the output power is reduced past ½ of the input power. Information technology is denoted by f2. Bandpass filter does not allow frequency later on this point, whereas the band stop filter allows it.
- Related Post: Types of Passive Depression Laissez passer Filters
Center Frequency f0
The frequency that lies at the middle of the passband or stopband in a bandpass filter or band reject filter respectively is called centre frequency. Information technology lies in-between the two cut-off frequency i.e. lower & Upper cut-off frequency. In fact, it is the arithmetic mean of both cut-off frequencies.
f0= (fone + f2) / 2
Bandwidth:
The range of frequencies that are passed (in case of bandpass filter) without whatsoever attenuation or the frequencies that are attenuated (in case of band decline filter) is chosen the bandwidth of the filter. The width of the frequencies before (in instance of low pass filter) or after (in case of high laissez passer filter) the cutoff frequency is called bandwidth
It is the difference betwixt both cutoff frequencies of the band pass or band reject filter.
Β = f2 – fi
Curl-Off Charge per unit;
Information technology is the rate of change of gain/ output power, the drop rate of gain of the filter is called the whorl-off rate. it is expressed as a gain loss per decade (ten times increase in frequency) or per octave (two-time increase in frequency).
The curlicue-off rate of nth order filter is 20n dB/decade or 6n dB/octave & n is the order of the filter. The per-decade means with a ten times increase in frequency & the octave ways a 2 times increase in frequency.
Types Of Filters:
In that location are different types of filters classified based on their frequency response and construction.
- Related Postal service: Types of Agile High Pass Filter
Based On Their Construction:
According to the construction of the filters, there are 2 types of filters i.e. Passive Filters & Active filter.
-
Passive Filters
Equally the name suggests, passive filters are made upward of passive components, such as resistors, capacitors & inductors.
Information technology does not need any external source of energy. Therefore at that place is no voltage gain in these filters. The output voltage is ever less than its input voltage.
Information technology tin can easily filter a high-frequency point only information technology cannot process whatever low frequencies.
Although its pattern is simple but connecting a load to this filter impacts on its characteristics. Cascading the passive filters for college gild filter affects the characteristics of the filter.
-
Active Filters
In add-on to the resistor & capacitor, Agile filter uses an agile component such as an operational amplifier, transistors, etc.
The downside is that information technology needs an external source of ability, only it provides a high voltage gain. This proceeds is used for amplifying any weak input signals.
The active filter tin filter very low-frequency signals but it cannot process very loftier-frequency signal.
They may have a little bit of circuitous design merely they provide very loftier input & depression output impedance. That is why; the load impedance does not touch on the characteristics of the active filters.
to increase the gild of the filter, active filters are used in cascading configuration without worrying near the loss of input signals power.
- Related Post: Different Types of Sensors with Applications
Based On Their Frequency Response:
The filters are classified based on the frequency response into the following four categories.
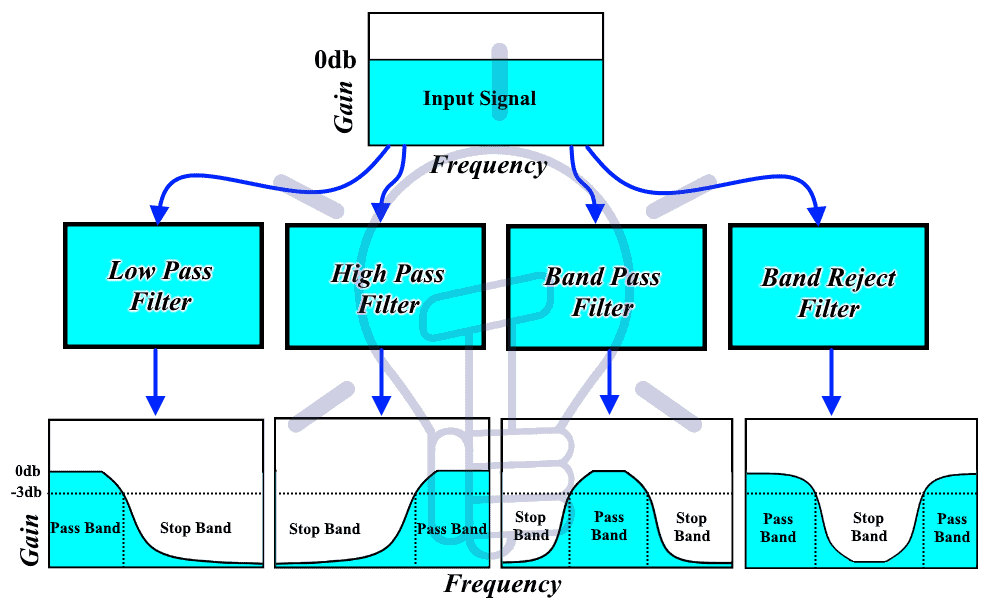
-
Low Pass Filter.
Depression Pass filter allow low-frequency signals without any attenuation (decrease in power) but it rejects whatever loftier-frequency signals.
The low pass filter has a reactive component, whose reactance varies with the input frequency. The variation in the reactance causes the voltage drib to increase or subtract within the circuit. if the voltage driblet is larger at the output, the signal will exist passed, otherwise, it is rejected past the filter.
The passband & stopband frequencies are defined past the cutoff frequency of the filter.
Any frequency less than the cutoff frequency is passed without any attenuation. While any other higher frequency indicate then the cutoff frequency will be blocked.
Related Mail service: Types of SSR Relays – Construction & Performance
-
High Pass Filter.
The type of filter that allows the high-frequency signals to pass without any attenuation in its amplitude & blocks (rejects) any low-frequency signal is called loftier laissez passer filter.
Any signal with a frequency lower than the cutoff frequency of the filter gets blocked. While any signal with a frequency college than the cutoff frequency passes with total amplitude.
Related Mail service: Types of Diodes and Their Applications
-
Band Pass Filter;
This type of filter allows a specific band of frequencies & blocks any other frequencies lower or higher than its passband frequencies.
This blazon of filter has two cutoff frequencies i.due east. lower & upper cutoff frequency.
Bandpass blocks low frequencies & high frequencies, while allows the frequencies in between known as the passband frequencies.
Any input betoken having frequency belonging to the passband frequencies will get passed without whatsoever attenuation.
Combining low pass filter & a high pass filter together in a pour configuration will provide a bandpass filter.
The low laissez passer filter will block high frequencies & the high pass volition block low frequency. & they will pass the middle frequencies in betwixt
Related Post: Types of Rectifiers and Their Functioning
-
Band Turn down Filter;
This type of filter attenuates the bespeak whose frequencies lies in a fixed ring of frequencies.
Information technology is besides known every bit Ring Stop filter or Notch Filter.
It works completely opposite to the bandpass filter. It allows depression-frequency indicate & high-frequency signals. But information technology does not allow a stock-still band of frequencies in between.
It also has lower & upper cutoff frequencies. And whatsoever signals having frequency in-between these cutoff frequencies are rejected by the filter.
- Related Post: Counter and Types of Electronic Counters
Applications Of Filters:
Frequency filters take and then many applications in our livelihood; some of these applications are given beneath;
- The tuner in radio: The bandpass filter in the tuner of the radio allows a fixed frequency to the output speaker.
- Treble & bass of the speaker: The bass has lower frequencies & treble has higher frequencies. They are separated using high laissez passer & low pass filter and are separately routed to corresponding bass speaker & treble speaker for clear music.
- Anti-Aliasing: information technology is a depression laissez passer filter that filters out the high-frequency components from a indicate earlier sampling. It prevents the aliasing component class being sampled.
- Notch Filter: they are band rejects filters with a narrow bandwidth that filter out any interfering signal.
- Power Supply Smoothing: The output of the ability supply which is a rectifier has an Air conditioning ripple in information technology. These frequencies are filtered out using a depression pass filter which results in smoothing the output indicate.
- Noise suppression: They are used in communication systems for noise removal from the received signals.
Related Posts:
- Types of Amplitude Modulation (AM) – Advantages & Disadvantages
- Types of Modulation Techniques used in Communication Systems
- Types of Resistive Sensors – Transducer, Potentiometer & Strain Gauge
What Is A Filter In Electrical Engineering,
Source: https://www.electricaltechnology.org/2019/06/types-of-filters.html
Posted by: montanoyousticheare.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is A Filter In Electrical Engineering"
Post a Comment